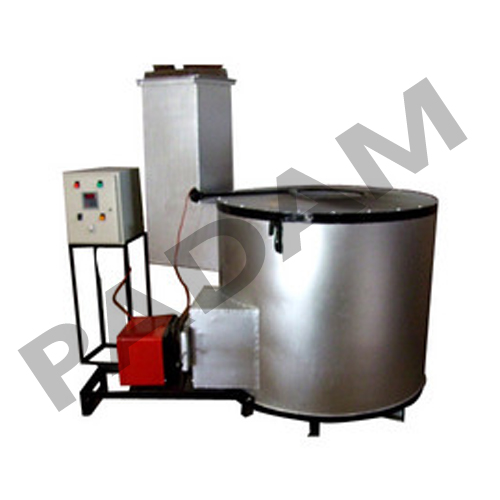
How an Oil-Fired Furnace Works
- Fuel Combustion - Oil is pumped into the burner and mixed with air for complete combustion.
- Heat Generation - The flame heats the refractory chamber, raising the temperature to the required level.
- Heat Transfer - The heat is transferred directly (for forging/melting) or indirectly (for heat treatment).
- Temperature Control - Automated thermocouples and controllers maintain precise heat levels.
- Exhaust & Efficiency Optimization - Waste gases exit through a chimney, and heat recovery systems improve efficiency.